Understanding the Differences Between Personal and Business Credit
Introduction to Personal and Business Credit
Understanding the differences between personal and business credit is crucial for anyone looking to manage their finances effectively. While both types of credit are essential for borrowing money, they serve different purposes and are evaluated differently by lenders.

What is Personal Credit?
Personal credit refers to the credit score and credit history associated with an individual. It reflects how well a person manages debt and finances. This credit score is used by lenders, such as banks and credit card companies, to determine the risk of lending money or extending credit to an individual.
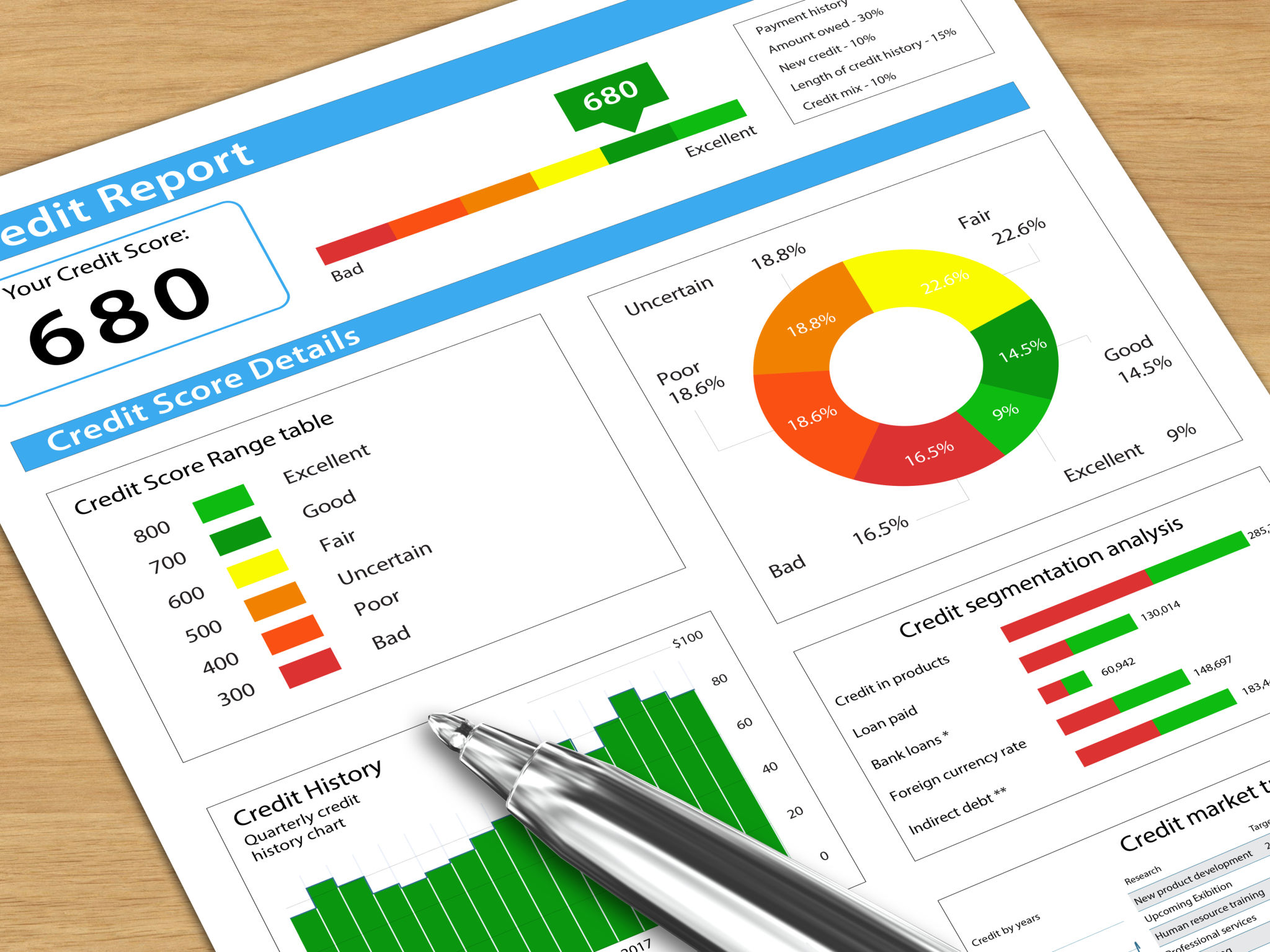
Personal credit scores typically range from 300 to 850. A higher score indicates better creditworthiness, making it easier for individuals to secure loans or get better terms on credit cards. Factors that impact personal credit scores include payment history, amount of debt, length of credit history, and types of credit used.
Understanding Business Credit
Business credit, on the other hand, is linked to a company rather than an individual. It is an important financial tool that helps businesses secure funding to grow and expand their operations. Business credit is used to evaluate a company's ability to repay debts and is crucial for obtaining business loans, leases, and lines of credit.
Business credit scores are generally based on the company's financial history, including payment history with suppliers and lenders, the amount of credit available, and the length of time the business has been operational.

Key Differences Between Personal and Business Credit
The primary difference between personal and business credit lies in who is responsible for the debt and how it affects one's financial standing. Here are some key distinctions:
- Responsibility: Personal credit is tied to an individual, while business credit is tied to a company.
- Impact: Personal credit affects an individual's ability to obtain personal loans or mortgages. Business credit affects a company's ability to secure business financing.
- Credit Reporting Agencies: Personal credit is monitored by agencies like Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. Business credit is often monitored by agencies such as Dun & Bradstreet, Experian Business, and Equifax Business.
Building Strong Personal and Business Credit
Both personal and business credit require responsible management to build and maintain a strong score. Here are some tips for building good credit:
- Pay bills on time to maintain a positive payment history.
- Keep debt levels manageable by not overextending your credit limits.
- Diversify your credit mix to show you can manage different types of debt responsibly.
- Review your credit reports regularly to correct any inaccuracies.
The Importance of Separating Personal and Business Finances
One of the most important aspects of managing both personal and business credit is keeping them separate. Mixing personal and business finances can lead to confusion and may negatively impact both your personal and business credit scores.
Using separate accounts for personal and business transactions not only helps in maintaining clear records but also ensures that any financial issues within your business do not affect your personal finances.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between personal and business credit is essential for effective financial management. By recognizing how each type of credit works, individuals and business owners can make informed decisions that will help them maintain strong financial health. Whether you're applying for a personal loan or seeking business financing, having a clear understanding of these concepts will put you in a better position to succeed financially.
